
To deal with tied ranks, the full version of Spearman correlation formula has to be used, which is a slightly modified version of Pearson's r:
d i is the difference between a pair of ranks. If there are no tied ranks, a simpler formula will do: It can be any value from -1 to 1, and the closer the absolute value of the coefficient to 1, the stronger the relationship:ĭepending on whether there are or there are no ties in the ranking (the same rank assigned to two or more observations), the Spearman correlation coefficient can be calculated with one of the following formulas. 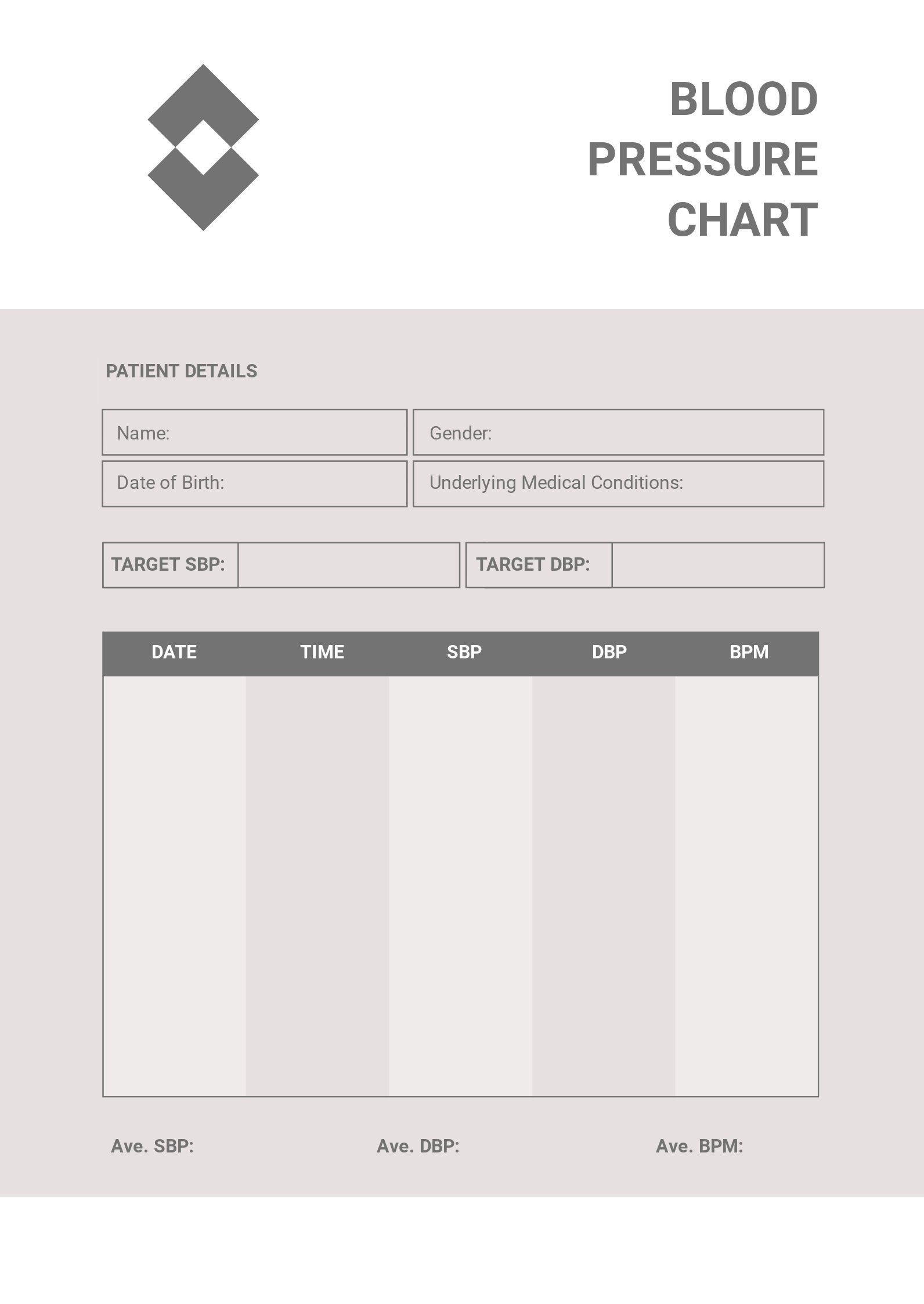
The Spearman rank correlation coefficient measures both the strength and direction of the relationship between the ranks of data.
In statistics, the Spearman correlation coefficient is represented by either r s or the Greek letter ρ ("rho"), which is why it is often called Spearman's rho.
Is the number of symptoms a patient has related to their willingness to take medication?. Are people with a higher level of education more concerned about the environment?. 
Unlike the Pearson correlation, the Spearman correlation is not sensitive to outliers because it performs calculations on the ranks, so the difference between actual values does not have meaning.įor example, you can use the Spearman correlation to find the answers to the following questions: If your values can be placed in "first, second, third…" order, you are dealing with ordinal data.
If your data exhibit a non-linear relationship or are not normally distributed. The Spearman correlation analysis is to be used in any of the following circumstances when the underlying assumptions of the Pearson correlation are not met: In a monotonic relationship, the variables also tend to change together, but not necessarily at a constant rate. Spearman Rank Correlation evaluates the monotonic relationship between the ranked values. Linear means a relationship when two variables change in the same direction at a constant rate. 
The Pearson Product Moment Correlation tests the linear relationship between two continuous variables. The Spearman correlation is the nonparametric version of the Pearson correlation coefficient that measure the degree of association between two variables based on their ranks.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
